In recent years, the use of Aluminum Radiator Extrusion Profiles has gained significant traction in various industries. According to a report from Research and Markets, the global market for aluminum radiators is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2021 to 2026. This rising demand reflects the enhanced thermal efficiency and lightweight properties of aluminum.
However, the performance of these profiles does not solely rely on their material. Factors such as extrusion process parameters, surface treatments, and design significantly impact their effectiveness. For instance, a study from the International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer highlights that optimizing the surface area can lead to a 15% improvement in heat dissipation.
Many manufacturers overlook these aspects, resulting in profiles that fail to deliver optimal performance. This oversight can lead to increased energy consumption and reduced lifespan, affecting overall sustainability efforts. It is essential to address these factors for both environmental and economic benefits. Embracing advancements in design and technology is a step toward maximizing the potential of Aluminum Radiator Extrusion Profiles.

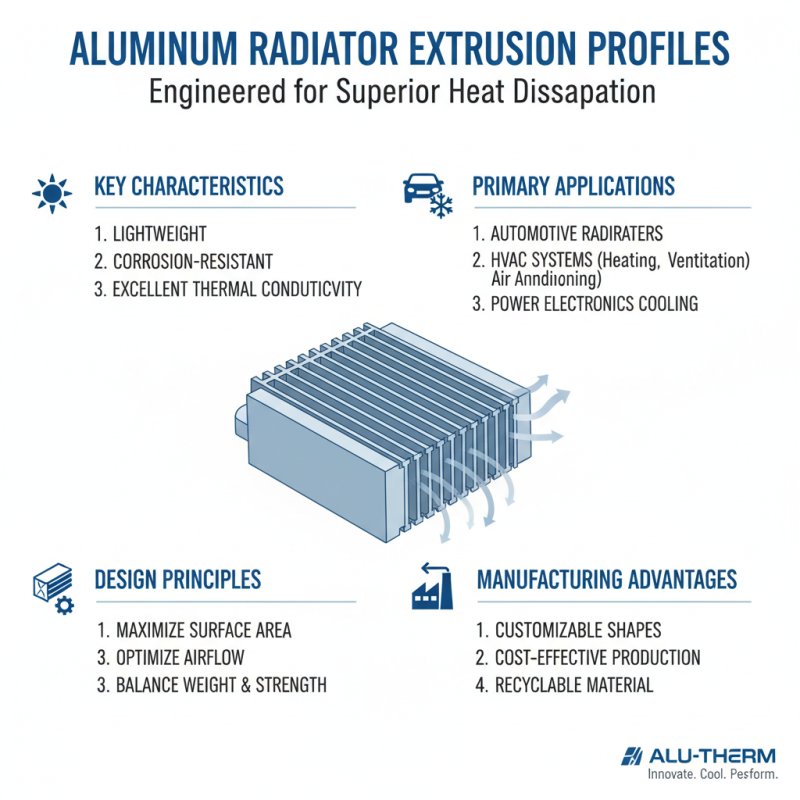
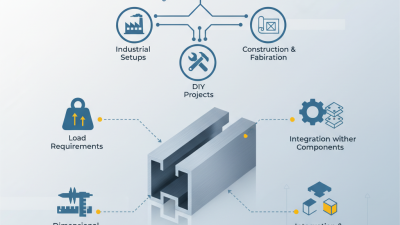
Aluminum radiator extrusion profiles have become essential in various applications, including automotive and HVAC systems. These profiles are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and have excellent thermal conductivity. Their design plays a crucial role in maximizing heat dissipation. Engineers often need to balance weight and strength, which can be challenging.
In automotive applications, aluminum extrusions help improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. They are used in various components, including radiators and cooling systems. However, efficiency can drop if the profiles are not designed correctly. It’s important to consider factors like surface area and airflow to enhance performance effectively.
In HVAC systems, aluminum extrusions provide durability and adaptability. Still, not all installations are perfect. Some systems may face challenges with air blockage or uneven heat distribution. Continuous improvement in design can help address these issues. Emphasizing precise manufacturing processes and comprehensive testing can lead to better outcomes. Understanding these profiles thoroughly is key to their effective use.
Aluminum radiators are essential in various industries, from automotive to HVAC. The performance of these radiators relies heavily on several key factors. One primary element is the extrusion profile design. Studies show that a well-designed profile can enhance heat transfer by 20-30%. However, many manufacturers overlook this aspect.
Another critical factor is the aluminum alloy used. Alloys like 6063 and 6061 present varying thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. According to industry reports, 6063 offers better workability, while 6061 provides higher strength. Selecting the right alloy can significantly affect lifetime performance. Unfortunately, some companies make choices based solely on cost rather than longevity.
Furthermore, the surface treatment process is vital. Treatments such as anodizing can improve durability and heat dissipation. Reports indicate that anodized finishes can enhance performance by up to 15%. However, inconsistent application can lead to uneven surfaces, affecting efficiency. It's essential for manufacturers to continually assess their processes.
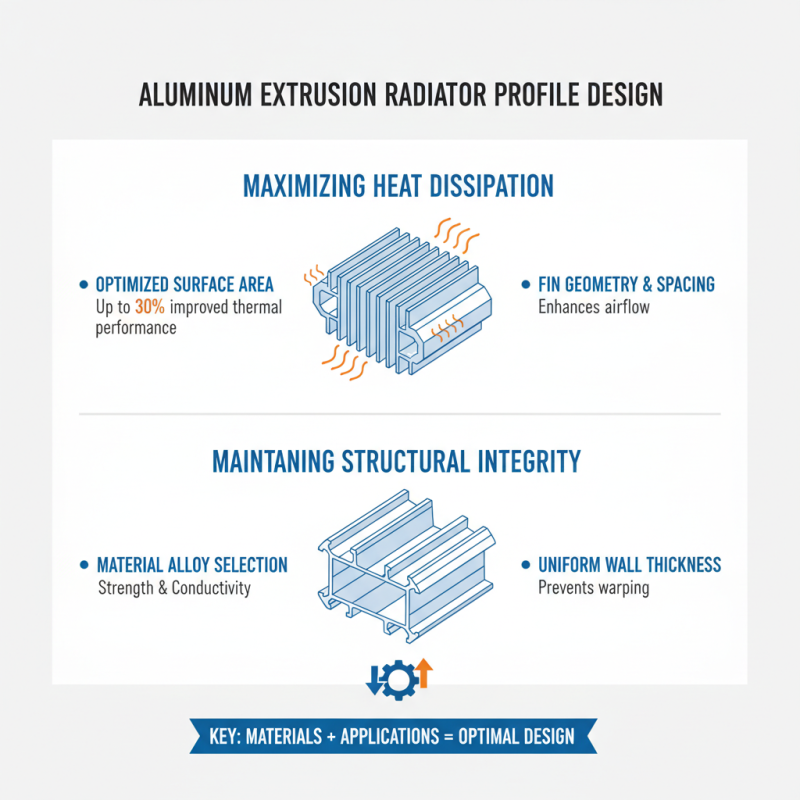
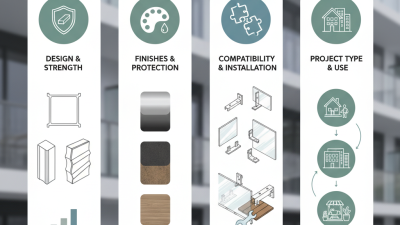
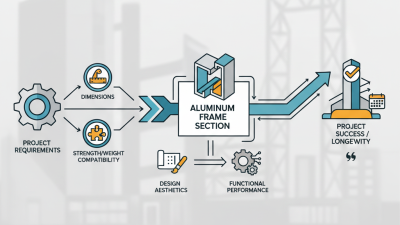
Designing aluminum extrusion profiles requires a keen understanding of both materials and applications. A well-designed radiator profile should maximize heat dissipation while maintaining structural integrity. According to industry reports, profiles with optimized surface areas can improve thermal performance by up to 30%. This underscores the importance of careful design choices.
Incorporating features like fins or grooves can enhance airflow, further increasing efficiency. However, intricate designs may complicate the manufacturing process. Balancing complexity with feasibility is crucial. Engineers must weigh the benefits of enhanced performance against potential production challenges. It's essential to understand the tolerance levels of the extrusion process to prevent defects.
Material selection also plays a critical role. The mechanical properties of aluminum alloys vary significantly; some alloys are better suited for high-temperature applications. Focusing on the intended use can minimize failures and prolong lifespan. Failure to consider these factors can lead to costly redesigns. The insights gathered from ongoing R&D indicate that even minor adjustments in profile geometry can lead to significant performance improvements. Always revisit and refine designs based on feedback and testing.
Surface treatments play a crucial role in enhancing radiator efficiency. Different techniques can improve heat transfer and corrosion resistance. These treatments can include anodizing, painting, or powder coating. Each process alters the material's surface properties.
Anodizing, for instance, enhances durability and protects against wear. However, it can sometimes lead to uneven surfaces. This may affect how well the radiator dissipates heat. Similarly, painting can create a barrier but might trap heat within layers. It’s important to choose the right surface treatment for optimal performance.
Testing different finishes is beneficial. Some treatments may look great but not perform as expected. Regularly evaluating the performance helps identify weaknesses. Small details often make a big difference in efficiency. Ensuring effective surface treatments is not just about aesthetics; it’s about maximizing functionality.
| Surface Treatment | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Corrosion Resistance (Rating) | Weight (kg/m²) | Cost (USD/m²) | Efficiency Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anodized | 205 | Excellent | 4.5 | 15 | 25 |
| Powder Coating | 190 | Good | 4.0 | 12 | 15 |
| Clear Coat | 200 | Very Good | 4.2 | 13 | 20 |
| Electrophoretic Deposition | 210 | Outstanding | 4.8 | 18 | 30 |
| Natural Finish | 180 | Fair | 4.1 | 10 | 10 |
Quality control is crucial in aluminum radiator manufacturing. Ensuring precise dimensions and surface finishes can significantly impact performance. A report by the Aluminum Association states that a mere 1% variance in thickness can reduce efficiency by up to 3%. Adhering to strict tolerances is not just recommended; it is necessary.
Inspection techniques matter. Regular checks during the extrusion process help identify defects early. Visual inspection, along with advanced methods like ultrasonic testing, can reveal internal flaws often missed by the naked eye. A survey found that 85% of manufacturers reported fewer failures with proactive quality checks. It’s a reminder of the importance of diligence.
Material choice is another area needing reflection. Many companies overlook the alloys used in their products. Every alloy behaves differently under heat and stress. For instance, certain alloys are more prone to corrosion. Selecting the right material is not simple; it requires careful analysis and testing. Balancing cost and performance is a common struggle. Quality control isn’t just a box to check; it demands ongoing effort and attention.